As avid travelers, we often find ourselves drawn to stunning bodies of water—lakes, rivers, and oceans. However, while we enjoy the beauty of these natural wonders, it’s crucial to understand the potential dangers associated with them, especially when it comes to electricity and water. In this comprehensive article, we will explore how far electricity travels in water, its implications for safety, and share personal experiences that highlight the importance of staying informed. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Electricity in Water
Electricity is a powerful force, and its behavior in water can be somewhat perplexing. To understand how far it travels, we first need to explore the properties of water and electricity.
The Conductivity of Water
Pure water is actually a poor conductor of electricity. However, the more impurities (such as salts and minerals) present in the water, the better it conducts electricity. This means that seawater, which is rich in salt, is a much better conductor than freshwater. When considering electrical hazards, this distinction is vital.

Factors Affecting Electrical Conductivity in Water
- Salinity: Higher salt concentrations increase conductivity.
- Temperature: Warmer water may conduct electricity better.
- Impurities: Metals and organic materials can enhance conductivity.
How Far Can Electricity Travel in Water?

The distance electricity can travel in water largely depends on several factors including conductivity, voltage, and environmental conditions. Typically, the maximum effective distance electricity can travel in water ranges from a few centimeters to several meters.
Distance Breakdown by Voltage
| Voltage Level | Distance in Freshwater | Distance in Saltwater |
|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage (up to 120V) | 1-3 meters | 3-5 meters |
| Medium Voltage (120V – 480V) | 3-5 meters | 5-10 meters |
| High Voltage (above 480V) | 5-10 meters | 10-30 meters |
This table illustrates how the type of water significantly influences how far electricity can travel, especially under different voltage levels.
Safety Considerations Around Water
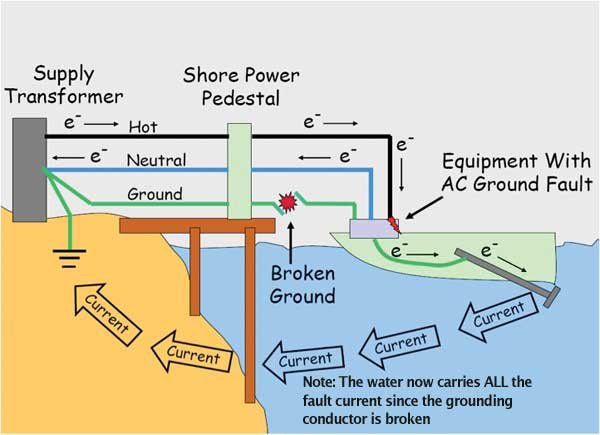
Understanding the distance electricity can travel through water is essential for safety, particularly for travelers enjoying water-related activities. Here are some key safety tips:
Travel Tips for Water Safety
- Stay Aware of Weather Conditions: Thunderstorms increase the risk of electrical hazards near water.
- Avoid Electrical Equipment: Do not use electrical devices near water bodies.
- Know Your Surroundings: Be mindful of overhead power lines when fishing or boating.
Personal Experiences: A Traveler’s Perspective
Reflecting on my travels, I recall a trip to the beautiful beaches of Costa Rica. The golden sands and rolling waves were mesmerizing. However, during a thunderstorm, I noticed how quickly the atmosphere changed. The locals stressed the importance of heading indoors during storms, as lightning strikes can be deadly. Always remember: water amplifies electrical risks.

Destination Highlights: Safe and Enjoyable Water Activities
Here are a few amazing travel destinations known for their incredible water activities—but remember to stay vigilant about electrical safety:

- Lake Tahoe, USA: Perfect for boating and fishing, but thunderstorms are common in summer.
- The Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Snorkeling in beautiful waters while always checking weather alerts.
- Playa del Carmen, Mexico: Known for its lively beaches, but be cautious during storms.
Pros and Cons of Water Activities
Pros
- Relaxation and enjoyment in natural beauty.
- Variety of activities: swimming, fishing, snorkeling.
- Great opportunities for photography and exploration.
Cons
- Risk of electrical hazards during storms.
- Potential for accidents related to tides and currents.
- Water quality concerns in certain areas.
FAQs About Electricity and Water Safety
How does electricity travel in water?
Electricity travels through water based on its conductivity, with factors like salinity and temperature influencing how far it can go. In saltwater, electricity can travel further than in freshwater due to its higher content of dissolved salts.
What should I do if I see lightning near water?
If you see lightning or hear thunder, immediately leave the water and seek shelter in a safe, enclosed building or vehicle. Avoid tall structures and stay away from metal objects.
Can electricity travel through the ocean to affect swimmers?
Yes, electricity can travel through the ocean, especially during thunderstorms. It’s important to heed safety warnings and avoid swimming during adverse weather conditions.
What safety measures should I take while enjoying water activities?
Always check the weather before heading out, avoid using electrical devices near water, and stay aware of your surroundings.
Conclusion: Stay Safe While Enjoying Water Activities
Understanding how far electricity travels in water is crucial for ensuring your safety while enjoying the beauty of lakes, rivers, and oceans. By being informed and following safety tips, you can fully enjoy your water adventures without the risk of electrical hazards. Remember, knowledge is power—and in this case, it can save lives. Happy travels!